Table of Contents
Flexible PCBs, also known as flex PCBs or bendable circuit boards, are revolutionizing electronics design. Their ability to bend, fold, and conform to complex 3D shapes makes them ideal for compact, lightweight, and innovative devices. In this guide, we explore the types of flexible circuit boards, their advantages, applications, and how to choose the right one for your project. Whether you’re an engineer, designer, or procurement specialist, this article provides actionable insights to leverage flex PCBs for cutting-edge electronics.
Why Flexible PCBs? The Future of Compact Electronics
As electronics become smaller and more integrated, flexible PCBs offer unmatched benefits over traditional rigid PCBs. Made from flexible substrates like polyimide, these circuits combine copper conductors with bendable materials to deliver:
- Space Optimization: Thin and flexible, they fit into tight spaces where rigid boards fail.
- Weight Reduction: Lighter than rigid PCBs, reducing connectors and cabling.
- Reliability: High resistance to vibration, temperature changes, and physical stress.
- Design Versatility: Conform to complex 3D shapes for innovative product designs.
From wearable technology to aerospace systems, flex PCBs are driving innovation across industries. Their growing demand in IoT devices, 5G technology, and medical electronics underscores their role in the future of compact electronics.
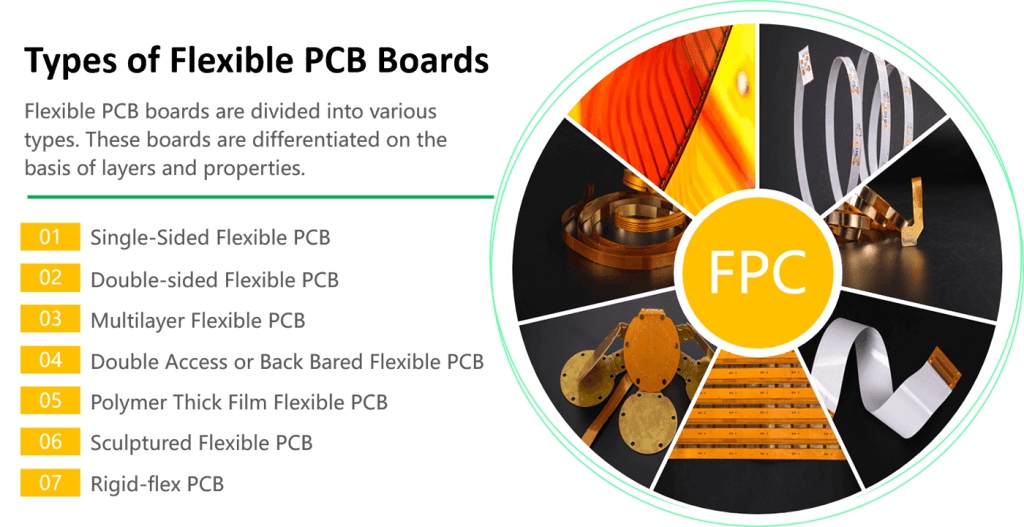
Types of Flexible Circuit Boards
Flexible PCBs are categorized based on layers and properties. Below, we explore the six main types, their advantages, and ideal applications.
1. Single-Sided Flexible PCB
Overview
Single-sided flexible PCBs feature one conductive copper layer on a flexible dielectric substrate, typically polyimide. They are the simplest and most cost-effective flex PCB type.
Advantages
- Cost-Effective: Ideal for budget-conscious projects with simple circuit needs.
- Excellent Flex Life: Supports dynamic bending and complex 3D shapes.
- Compact and Lightweight: Perfect for space-constrained designs.
- Versatile Applications: Used in low-density circuits requiring flexibility.
Applications
- Wearable Technology: Smartwatches and fitness trackers.
- Bendable Displays: Flexible screens in consumer electronics.
- Portable Medical Devices: Compact diagnostic tools.
Why Choose Single-Sided Flex PCBs?
Single-sided flex PCBs are best for straightforward designs where cost and flexibility are priorities. For example, a recent project at JHYPCB used single-sided flex PCBs to develop a lightweight wearable sensor, reducing production costs by 20% while maintaining reliability.

Single sided Flexible PCB
This is the simplest flexible PCB type with only one conductive layer. A thin flexible dielectric film, such as Polyimide, is used. There is only one conductive layer on the board.
2. Double-Sided Flexible PCB
Overview
Double-sided flexible PCBs have two conductive copper layers, one on each side of the flexible substrate, enabling components and traces on both sides.
Advantages
- Higher Routing Density: Supports more complex circuits than single-sided PCBs.
- Compact Functionality: Integrates more features in a small footprint.
- Cost-Effective for Mid-Complexity: Balances performance and cost.
- Dynamic Flexibility: Maintains bendability for 3D applications.
Applications
- Medical Devices: Portable monitors and imaging equipment.
- Wearable Electronics: Smart clothing and IoT devices.
- Aerospace Systems: Rugged, flexible circuits for satellites.
Double Sided Flexible PCBs - More Routing Density
Double-sided flexible PCBs have two conductive layers, one on each surface. You have components or conductive lines on both sides. These flexible circuits are more economical compared to single-sided flexible PCBs.
3. Multilayer Flexible PCB
Overview
Multilayer flex PCBs feature three or more copper layers separated by thin polyimide films, interconnected via plated through-holes (vias).
Advantages
- Unmatched Wiring Density: Supports complex, high-density circuits.
- Enhanced Signal Integrity: Ideal for high-performance electronics.
- 3D Formability: Conforms to intricate shapes without compromising functionality.
- Reliability: Built for demanding environments with excellent flex life.
Applications
- Aerospace and Defense: Avionics and radar systems.
- Medical Devices: Advanced imaging and diagnostic equipment.
- Automotive Electronics: High-performance control units.
Why Multilayer Flex PCBs?
For cutting-edge applications, multilayer flex PCBs deliver unparalleled performance. Their ability to support complex circuitry makes them a top choice for next-generation electronics.
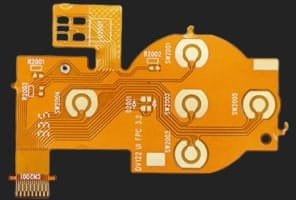
Multilayer Flexible PCBs - Ultimate Routing Density
In a multilayer flexible PCB, there are multiple conductive layers of copper. It has at least three copper/conductive layers or more. There is a thin layer of PI between two conductive layers. These layers are interconnected with the help of vias.
4. Double Access/Back-Bared Flexible PCB
Overview
Double-access or back-bared flex PCBs are single-sided circuits with a unique design that exposes copper traces on both sides, allowing dual-sided access.
Advantages
- Cost Savings: Cheaper than true double-sided PCBs.
- Dual-Sided Access: Supports component mounting and testing on both sides.
- Flexible Form Factor: Retains single-layer flexibility.
- Moderate Complexity: Ideal for cost-sensitive, mid-complexity designs.
Applications
- Consumer Electronics: Wearables and IoT sensors.
- Medical Sensors: Disposable diagnostic devices.
- Industrial Controls: Compact instrumentation.
Unique Insight
Back-bared flex PCBs are gaining traction in disposable medical devices due to their cost-effectiveness and flexibility. At JHYPCB, we’ve optimized back-bared designs to reduce manufacturing costs by 15% for a client’s single-use glucose monitor.

Double Access/Back Bared Flexible PCBs - Dual-Sided Value
Dual access or back bare flexible PCB is a particular type of single-sided flexible circuit. There is only one layer of copper, but it is arranged in a special manner to be accessed from both sides. This is the specialty of a dual-access flexible circuit.
5. Polymer Thick Film (PTF) Flexible PCB
Overview
Polymer Thick Film (PTF) flex PCBs use conductive polymer inks printed onto flexible substrates like polyimide or polyester, replacing traditional copper laminates.
Advantages
- Fine Trace Geometries: Enables intricate circuit patterns.
- 3D Circuit Layouts: Conforms to curved surfaces.
- Eco-Friendly: Avoids harsh etchants used in copper-based PCBs.
- Cost-Effective: Lower fabrication costs for specific applications.
Applications
- Flexible Displays: Curved screens and e-paper.
- Wearable Electronics: E-textiles and smart fabrics.
- Disposable Sensors: Single-use medical and IoT devices.
Industry Trend
PTF flex PCBs are at the forefront of printed electronics, with growing applications in 6G technology and smart packaging. Their eco-friendly manufacturing aligns with sustainability trends, making them a future-proof choice.
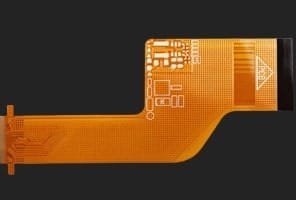
Polymer Thick Film Flexible PCBs - Printed Circuitry
Polymer Thick Film (PTF) flexible circuits are real printed circuits. Several types of conductive inks are used to print the circuit on the base. Most of the time, the ink is applied with the help of stencils. Most of the time, the ink is applied with the help of stencils.
6. Rigid-Flex PCB
Overview
Rigid-flex PCBs combine flexible and rigid substrates, integrating flexible circuits with rigid board sections for seamless functionality.
Advantages
- Hybrid Design: Combines flexibility with rigid board stability.
- High Reliability: Ideal for rugged, high-vibration environments.
- Compact Integration: Reduces connectors and cabling.
- Versatile Applications: Supports complex, high-density designs.
Applications
- Aerospace Systems: Avionics and satellite modules.
- Medical Devices: Implantable devices and imaging systems.
- Consumer Electronics: Foldable smartphones and tablets.
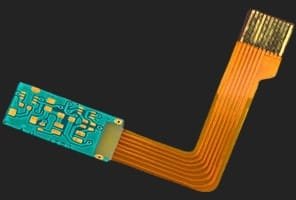
Rigid-Flex PCBs - Seamless Integration of Flex and Rigid
A rigid-flex PCB is a combination of rigid PCBs and flexible PCBs. There can be multiple rigid and flexible parts to create one circuit. The flexible part can bend easily, and the rigid part takes up the required space. Usually, the rigid parts are connected via flexible circuits.
How to Choose the Right Flexible PCB Type
Selecting the appropriate flex PCB depends on your project’s requirements:
- Cost Constraints: Single-sided or back-bared flex PCBs for budget-friendly designs.
- Circuit Complexity: Double-sided or multilayer flex PCBs for intricate circuits.
- Environmental Demands: Rigid-flex or multilayer PCBs for rugged applications.
- Sustainability Needs: PTF flex PCBs for eco-friendly designs.
Comparison Table
| Type | Layers | Cost | Complexity | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided | 1 | Low | Low | Wearables, Displays |
| Double-Sided | 2 | Medium | Medium | Medical, Aerospace |
| Multilayer | 3+ | High | High | Defense, Automotive |
| Double Access | 1 | Low | Medium | IoT, Disposable Sensors |
| Polymer Thick Film | 1 | Medium | Low-Medium | E-textiles, Flexible Displays |
| Rigid-Flex | Mixed | High | High | Smartphones, Avionics |
Manufacturing Flexible PCBs: Key Processes
Flexible PCBs rely on specialized materials and processes:
- Base Materials: Polyimide, polyester, or polyethylene naphthalene for flexibility and thermal stability.
- Copper Lamination: Thin copper foils (9μm to standard) bonded with adhesives or vacuum lamination.
- Circuit Formation: Etching for copper-based PCBs or printing for PTF circuits.
- Supporting Processes: Laser cutting, via plating, SMT assembly, and conformal coatings.
For rigid-flex PCBs, selective stiffeners (e.g., epoxy or metal plates) create rigid sections, ensuring seamless integration.
FAQs About Flexible PCBs
Flex PCBs offer space savings, weight reduction, dynamic flexibility, and reliability in tight or rugged environments.
Flexible substrates like polyimide or polyester, with copper foils or conductive inks for circuitry.
When properly designed, flex PCBs withstand bending, twisting, and vibrations, enhanced by protective coatings.
Consumer electronics, medical, aerospace, automotive, and wearables rely on flex PCBs for compact, reliable designs.
Single and double-sided flex PCBs are cost-effective; multilayer and rigid-flex designs are pricier due to complexity.
Why Choose JHYPCB for Flexible PCBs?
With over 15 years of experience in PCB manufacturing, JHYPCB delivers high-quality flexible circuit boards tailored to your needs. Our cutting-edge technology and expert team ensure precision, reliability, and cost-efficiency. Ready to explore flex PCBs for your next project? Contact us or request a quote today!
Related Posts
- Custom Flex PCB:Tailored Solutions for Your Applications
- Custom PCB Fabrication in China – Prototyping & Mass Production
- Expedited PCB Services – Quick Turnaround for Your Urgent Needs
- JHYPCB: The Best Prototype PCB Manufacturer for Your Needs
- Rapid PCB Prototyping Services: A Comprehensive Introduction
- Introduction to Semi-Flex PCBs: Bridging Rigid and Flex PCBs
- How to Select the Right Flexible PCB Manufacturer for Your Product: A 6-Step Guide
- Layer Stackup in Rigid-Flex PCB
- Why is Flexible PCB so Expensive?
- The Manufacturing Process Of Double-sided Flexible PCB Coverlay
- What Are The Advantages And Applications Of Rigid-Flex PCBs?
- Rigid PCB vs Flex PCB: What Is The Difference?
- How to Solder On Flex PCB?
- Flexible Printed Circuit For Today’s Packaging
- 16 Factors Affecting The Cost And Price of Flexible PCB
- Complete Introduction of Flexible Circuit Board Materials
- The terms you have to know related to the manufacture of Flexible PCB
- Knowledge of Flexible PCB Manufacturing Process Steps
- Knowledge of Plating on Flexible Circuit Board Surface
- Five factors that FPC PCB designers should know about impedance control
- Key Process Flow of Rigid-Fled PCB Production